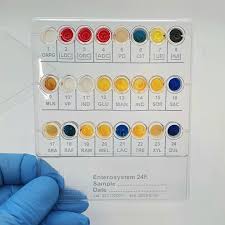
Liofilchem® Enterosystem 24R, for 20 Tests
Catalog No :
CAS Number :
Brand :
In Stock
Specifications:
| Application | Clinical microbiology |
| Storage Temperature | 2-8°C |
| Product Type | Microbial ID System |
| Product Brand | Liofilchem |
| Product Grade | Microbiology grade |
The Liofilchem® Enterosystem 24R is a 24-well system designed for the identification of Gram-negative, oxidase-negative enterobacteria, specifically members of the Enterobacteriaceae family. The system uses desiccated biochemical substrates in individual wells, and identification is based on the colorimetric results of metabolic reactions. These results form an 8-digit numerical profile for organism identification through Liofilchem’s online software.
System Features
- Comprehensive Testing:
- 24 distinct biochemical tests covering enzyme activity, sugar utilization, and gas production.
- Includes specialized tests like lysine/ornithine/arginine decarboxylation, ONPG hydrolysis, citrate utilization, urea hydrolysis, and hydrogen sulfide production.
- Broad Application:
- Designed for clinical diagnostics of Gram-negative bacteria, with a focus on oxidase-negative species.
- Compatible with a wide range of Enterobacteriaceae and other related organisms.
- Ease of Interpretation:
- Color changes are easy to interpret using the provided Interpretive Table.
- An 8-digit numerical profile simplifies identification.
- User Tools:
- Free online identification software allows accurate organism determination.
Contents of the System
- Product Codes: Ref. 71619 (20 tests), Ref. 79619 (4 tests).
- Each kit contains:
- Enterosystem 24R wells.
- Vials of physiological solution (7.0 mL per vial).
- Cartridges containing 20 discs each for xylose and arabinose tests.
- Instructions and data chart.
Test Procedure
- Preparation:
- Isolate the microorganism on a suitable growth medium (e.g., MacConkey Agar, EMB Agar).
- Ensure the organism is Gram-negative and oxidase-negative through preliminary tests.
- Prepare a bacterial suspension at 0.5 McFarland standard.
- Inoculation:
- Dispense 0.2 mL of the bacterial suspension into each well.
- Add the required xylose and arabinose discs to specific wells.
- Overlay specific wells with vaseline oil to maintain anaerobic conditions.
- Incubation:
- Incubate at 36±1°C for 18-24 hours.
- Result Interpretation:
- Observe color changes and compare them to the Interpretive Table.
- Perform additional steps (e.g., VP and indole tests) by adding reagents.
- Record results to generate an 8-digit code.
5. Identification:
- Use the online ID Software to match the biochemical code to the corresponding bacterial species.
Interpretive Table
| Test | Positive Reaction | Negative Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| ONPG | Yellow | Colorless |
| LDC (Lysine) | Red | Yellow-Orange |
| ODC (Ornithine) | Red | Yellow-Orange |
| ADC (Arginine) | Red | Yellow-Orange |
| PD | Black-Brown | Yellow |
| CIT | Blue-Dark Green | Light Green |
| UR (Urea) | Red-Fuchsia | Yellow-Orange |
| H2S | Black | Yellow |
| MLN | Blue-Green | Yellow |
| VP (Acetoin) | Pink-Red | Yellow |
| IND (Indole) | Red Ring | Yellow |
| GLU | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| MAN (Mannitol) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| INO (Inositol) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| SOR (Sorbitol) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| SAC (Saccharose) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| ARA (Arabinose) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| RAF (Raffinose) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| RAM (Rhamnose) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| MEL (Melibiose) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| LAC (Lactose) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| TRE (Trehalose) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| XYL (Xylose) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
| DUL (Dulcitol) | Yellow | Blue-Green |
Numerical Code Formation
The tests are grouped into 8 clusters of 3, with each test in the group assigned a value:
- 1: First test positive.
- 2: Second test positive.
- 4: Third test positive.
- 0: Negative test.
The sum of the values in each cluster forms an 8-digit numerical profile used for identification.
Quality Control
- Tested against reference strains:
- Escherichia coli ATCC 25922.
- Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028.
- Proteus mirabilis ATCC 25933.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883.
- Enterobacter cloacae ATCC 13047.
Storage and Disposal
- Storage: 2-8°C in original packaging.
- Disposal: Decontaminate and dispose of used materials following biohazard protocols.
Applications
- Clinical microbiology for enteric bacteria identification.
- Quality control in food and water safety.
- Research settings for enterobacteria characterization.
Comparison with API 20E
The Enterosystem 24R offers additional tests like raffinose and dulcitol utilization, giving broader differentiation within Enterobacteriaceae. While the API 20E integrates more streamlined testing, the Enterosystem 24R is cost-effective and suited for labs requiring comprehensive testing capabilities.
Comparison of Enterosystem 24R and Enterosystem 18R
| Feature | Enterosystem 24R | Enterosystem 18R |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Identification of Gram-negative, oxidase-negative enterobacteria | Identification of Gram-negative enterobacteria with simpler test profiles |
| Number of Biochemical Tests | 24 tests | 18 tests |
| Range of Tests | Includes broader substrate utilization and additional metabolic tests (e.g., raffinose, dulcitol, trehalose) | Limited to core metabolic and biochemical tests for enterobacteria |
| Well Configuration | 24 wells, including tests for decarboxylation, deamination, sugar utilization, and gas production | 18 wells with a more limited scope, focusing on basic biochemical reactions |
| Unique Features | - Incorporates xylose and arabinose discs for added identification capabilities - Extended substrate utilization like raffinose and dulcitol | - Simpler, fewer tests make it faster and more cost-effective for basic diagnostics |
| Application Complexity | More complex testing procedure with additional reagents and discs | Simpler testing process for routine identification |
| Target Organisms | Broader range of Enterobacteriaceae and other Gram-negative enterobacteria | Focused on common Enterobacteriaceae like E. coli, Klebsiella, and Proteus |
| Numerical Profile | Generates a 24-reaction-based numerical profile for species identification | Generates an 18-reaction-based numerical profile for species identification |
| Identification Software | Utilizes Liofilchem's online software for species identification based on a more detailed profile | Also uses online software but with fewer variables in the identification process |
| Preparation | Requires additional discs (arabinose and xylose) and specific reagents like vaseline oil for some tests | Requires fewer reagents and steps, making it less resource-intensive |
| Inoculation | Requires 0.2 mL bacterial suspension per well; overlay specific wells with vaseline oil | Similar inoculation method, but fewer wells simplify the procedure |
| Interpretation of Results | More detailed interpretive table with expanded differentiation capabilities | Basic interpretive table suitable for routine microbiology diagnostics |
| Quality Control Organisms | Includes additional organisms for quality control such as Enterobacter cloacae ATCC 13047 and Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | Quality control for common enteric pathogens like Salmonella Typhimurium and Proteus mirabilis |
| Best Suited For | Laboratories requiring comprehensive differentiation within Enterobacteriaceae or rare enteric bacteria | Laboratories needing fast, routine identification of common Gram-negative pathogens |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Higher cost due to more tests and complexity | Lower cost, ideal for routine and high-throughput diagnostics |
Key Differentiating Features:
- Broader Differentiation:
- Enterosystem 24R can distinguish a wider range of enterobacteria due to its additional tests like xylose, dulcitol, raffinose, and trehalose utilization.
- Enterosystem 18R focuses on essential biochemical reactions, making it ideal for routine diagnostics but with less differentiation power.
- Applications:
- Enterosystem 24R: Research settings or specialized labs for detailed microbial identification.
- Enterosystem 18R: Basic clinical labs or routine diagnostics for commonly encountered pathogens.
- Complexity vs. Simplicity:
- The 24R system is more complex and time-intensive but provides a higher resolution of species identification.
- The 18R system is simpler and faster, suitable for labs with limited resources.
Summary:
- The Enterosystem 24R is better suited for advanced laboratories needing a comprehensive microbial identification system, particularly when working with diverse or challenging samples.
- The Enterosystem 18R is ideal for laboratories requiring cost-effective, routine identification of common enteric pathogens.




 0
0