Specifications:
| Application | cell Signalling | ||
| Storage Temperature | Room Temperature | ||
| Product Type | Enzymes and Substrates | Forms | Solid |
| Product Brand | MedChem Express | ||
| Product Grade | Molecular Biology | ||
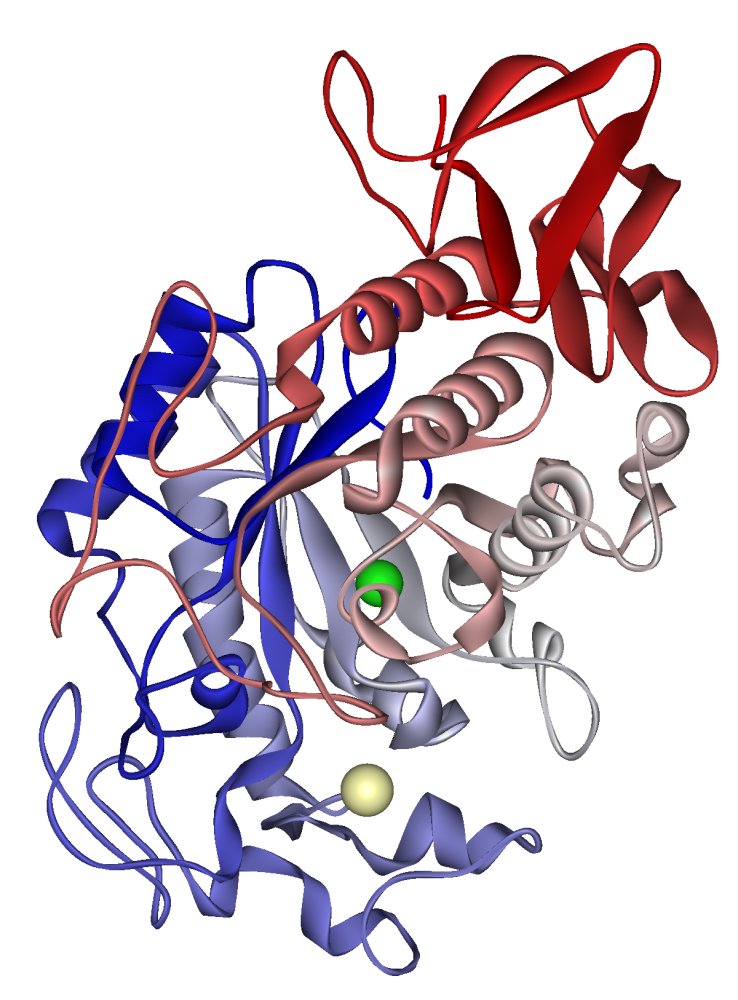
MCE α-Amylase is a high-quality hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of internal α-1,4-glycosidic bonds in starch, generating smaller saccharides such as maltose, glucose, and dextrins. This enzyme is widely used in biochemical research, carbohydrate metabolism studies, industrial process modeling, and enzymatic hydrolysis applications.
Produced by microorganisms—including bacteria, fungi, and genetically engineered strains—α-Amylase is a calcium-dependent metalloenzyme, requiring Ca²⁺ ions for structural stability and catalytic activity. Its functional relevance spans food processing, biotechnology, fermentation science, and enzymology research, making it one of the most widely studied and applied digestive enzymes.
Key Features
- High-purity α-amylase enzyme, suitable for in vitro enzymatic assays.
- Catalyzes hydrolysis of internal α-1,4-glycosidic linkages in starch.
- Produces key hydrolysis products: maltose, glucose, oligosaccharides.
- Derived from microbial sources such as Aeromonas hydrophila and other microorganisms.
- Stable and active over a wide pH and temperature range (dependent on source).
- Important research tool in carbohydrate metabolism, biotechnology, and enzymatic hydrolysis.
- Provided as a solid powder (white to light yellow).
- For research use only.
Scientific Background
α-Amylase plays a central role in starch degradation, making it indispensable in:
- Food & beverage industries
- Brewing and distilling
- Production of high-glucose and high-fructose syrups
- Fermentation processes
- Detergent formulation
- Paper and textile processing
Historically, starch hydrolysis relied on acid hydrolysis, but enzymatic catalysis using α-amylase offers:
- Greater efficiency
- Lower energy consumption
- Reduced byproducts
- Higher specificity
Plant-derived α-amylase has been isolated from barley, rice, and other cereal crops. Novel sources such as cassava mash wastewater have demonstrated broad pH and temperature tolerance, highlighting the enzyme’s versatility in industrial and environmental applications.
In Vitro Use
- Suitable for enzymatic digestion of starch under controlled laboratory conditions.
-
Can be used in studies involving:
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Enzyme kinetics
- Substrate-specificity assays
- Comparative enzyme activity profiling
- Requires calcium ions for optimal function (typical of metalloenzymes).
- Not intended for therapeutic use.
MCE notes that assay conditions reported in the literature are for reference only and should be optimized by users.
Clinical Context
A clinical trial reference (NCT02192892) highlights the investigation of enzymes such as α-amylase in malnutrition intervention programs, although the product itself is strictly for research use and not intended for clinical or therapeutic application.
Technical Specifications
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Product Name | α-Amylase |
| Brand | MedChemExpress (MCE) |
| Cat. No. | HY-B2193 |
| CAS Number | 9000-90-2 |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Color | White to Light Yellow |
| Initial Source | Microorganisms (e.g., Aeromonas hydrophila) |
| Structure Classification | Hydrolase enzyme |
| Function | Hydrolyzes α-1,4-glycosidic linkages in starch |
| Form | Powder |
| For Research Use | Yes (Not for clinical use) |
MCE α-Amylase (HY-B2193) is a versatile, high-quality enzyme ideal for biochemical, enzymatic, and industrial research requiring reliable starch hydrolysis activity. Its microbial origin, calcium-dependent catalytic mechanism, and suitability for a wide range of laboratory applications make it an essential reagent for researchers studying carbohydrate metabolism, enzyme kinetics, starch conversion, and fermentation processes. With consistent performance and broad applicability, it serves as a valuable tool in both academic and industrial research settings.
- Pack Size: 1g 500mg




 0
0