Liofilchem® ESBL (Chromosomal & Inducible AmpC) Disc Kit, EUCAST Compliant, 100 Tests
Catalog No :
CAS Number :
Brand :
In Stock
Specifications:
| Application | Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Resistance Testing (AST) |
| Storage Temperature | -20°C |
| Product Type | Antibiotic Disc |
| Product Brand | Liofilchem |
| Product Grade | Microbiology grade |
The Liofilchem® ESBL (Chromos. Ind. AmpC) Disc Kit is a specialized diagnostic tool designed for confirming the presence of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-producing bacteria in organisms with chromosomally encoded inducible AmpC β-lactamases.
This disc diffusion-based test differentiates between ESBL producers and non-ESBL-producing resistant strains by detecting synergy between cefepime (FEP) and cefepime + clavulanic acid (FEL). It is compliant with EUCAST (European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing) guidelines and is widely used in clinical microbiology laboratories for antibiotic resistance surveillance.
Key Features & Benefits
✔ Reliable & Accurate – Provides a clear distinction between ESBL and AmpC-producing bacteria.
✔ EUCAST Compliant – Follows international guidelines for antibiotic resistance detection.
✔ Easy-to-Use – Uses a disc diffusion method for quick and efficient interpretation.
✔ Supports Antimicrobial Stewardship – Helps in infection control and epidemiological surveillance.
✔ Essential for Clinicians – Assists in selecting effective β-lactam antibiotics for resistant infections.
Background: Understanding ESBL and AmpC β-Lactamases
1. What are ESBLs?
Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases (ESBLs) are Ambler Class A β-lactamases that hydrolyze penicillins, cephalosporins (including oxyimino-β-lactams), and monobactams, but not cephamycins or carbapenems.
- ESBLs are inhibited by β-lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam.
-
Common ESBL-producing bacteria:
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Other Enterobacteriaceae species
ESBL detection is mandatory in many healthcare settings for infection control and proper antibiotic selection.
2. What is Chromosomal Inducible AmpC β-Lactamase?
AmpC β-lactamases are Class C β-lactamases that hydrolyze penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins (e.g., cefoxitin, cefotetan), and oxyiminocephalosporins (e.g., ceftazidime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone) but not carbapenems.
- AmpC enzymes are weakly inhibited by clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam.
- Some Enterobacteriaceae species have chromosomally encoded inducible AmpC genes, which overexpress in response to β-lactam exposure, leading to resistance.
Common AmpC producers include:
- Enterobacter cloacae
- Enterobacter aerogenes
- Citrobacter freundii
- Serratia marcescens
- Morganella morganii
3. Why is Differentiation Between ESBL and AmpC Important?
- AmpC-producing organisms may appear resistant to third-generation cephalosporins but do not respond to clavulanic acid-based confirmatory tests.
- Some organisms harbor both ESBL and AmpC enzymes, making detection challenging.
- Cefepime (FEP) is the key antibiotic used in this test because it resists AmpC hydrolysis but remains sensitive to ESBL activity.
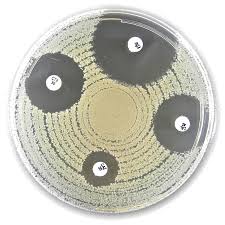
Principle of the ESBL (Chromos. Ind. AmpC) Disc Test
The Liofilchem® ESBL (Chromos. Ind. AmpC) Disc Kit works by comparing the inhibition zones of cefepime (FEP) alone versus cefepime + clavulanic acid (FEL).
Mechanism of Action
- Clavulanic acid inhibits ESBL enzymes, allowing for an increase in the inhibition zone when tested with cefepime (FEL disc).
- If the bacterial strain produces AmpC but not ESBL, there will be no significant difference between FEP (cefepime alone) and FEL (cefepime + clavulanic acid).
- If the strain produces both ESBL and AmpC, an increase in inhibition zone (≥5 mm) with FEL confirms ESBL presence.
This method ensures accurate differentiation between AmpC-only, ESBL-only, and dual ESBL-AmpC-producing strains.
Kit Contents & Specifications
The Liofilchem® ESBL (Chromos. Ind. AmpC) Disc Kit includes:
✅ 4 x 50 disc cartridges (total 200 discs)
✅ Individually packaged blister packs with a desiccant to maintain stability
✅ Disc types & concentrations:
- Cefepime 30 μg (FEP) – 50 discs
- Cefepime + Clavulanic Acid (30+10 μg) (FEL) – 50 discs
Test Procedure: Step-by-Step Guide
1. Sample Preparation
- Use a fresh, pure culture of the test organism.
- Prepare a bacterial suspension equivalent to 0.5 McFarland Standard.
- Use a sterile cotton swab to evenly inoculate a Mueller-Hinton agar plate.
2. Disc Application
-
Apply the following discs:
- FEP (Cefepime 30 µg)
- FEL (Cefepime + Clavulanic Acid 30+10 µg)
- Ensure sufficient spacing between discs to allow for accurate zone measurement.
3. Incubation
- Incubate the plate at 35 ± 1°C for 16-20 hours.
4. Interpretation of Results
After incubation, measure the zones of inhibition around each disc:
✅ ESBL Positive:
- Increase in inhibition zone ≥ 5 mm for FEL vs. FEP
❌ ESBL Negative (AmpC Only):
- No significant difference (< 5 mm) in inhibition zones
Quality Control Strains for ESBL Testing
- Positive Control: Escherichia coli NCTC 13353 (CTX-M-15 ESBL Producer)
- Negative Control: Escherichia coli ATCC® 25922 (Non-ESBL)
Applications & Use Cases
1. Clinical Microbiology Laboratories
- Hospitals & diagnostic labs use the test to confirm ESBL production in multidrug-resistant (MDR) Enterobacteriaceae.
- Helps prevent treatment failures by identifying resistant bacterial strains.
2. Infection Control & Antibiotic Stewardship
- Differentiates AmpC-producing bacteria from ESBL producers, guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy.
- Supports antimicrobial resistance (AMR) surveillance programs.
3. Pharmaceutical Research
- Used in pharmaceutical microbiology to test new antibiotics against ESBL-producing bacteria.
Limitations & Precautions
🔸 In vitro test – Cannot fully replicate in vivo conditions.
🔸 Several variables influence results, including media composition, incubation conditions, and disc potency.
🔸 Used only by trained professionals in microbiology laboratories.
🔸 Storage:
- Unopened: Store at -20°C to +8°C (until expiry date).
- Opened cartridges: Store at 2-8°C for up to 7 days.
Ordering Information
| Description | Packaging | REF | No. of Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cefepime 30 μg (FEP) | 1 x 50 Discs | 99006 | 50 |
| Cefepime + Clavulanic Acid (FEL) | 1 x 50 Discs | 99006 | 50 |
The Liofilchem® ESBL (Chromos. Ind. AmpC) Disc Kit is an essential diagnostic tool for microbiologists to detect and confirm ESBL-producing organisms, ensuring effective antibiotic therapy and infection control.




 0
0