Liofilchem® Teicoplanin TEC Antimicrobial Susceptibility Discs, 30 µg
Catalog No :
CAS Number :
Brand :
In Stock
Specifications:
| Application | Microbiology |
| Storage Temperature | 2-8°C |
| Product Type | Antibiotic Disc |
| Product Brand | Liofilchem |
| Product Grade | Microbiology grade |
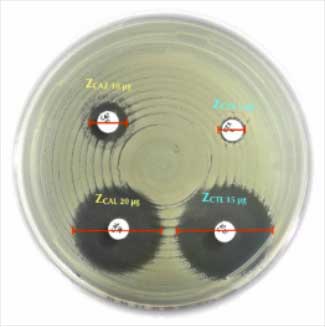
The Liofilchem® Teicoplanin TEC Antimicrobial Susceptibility Discs (30 µg) are standardized discs used for determining the antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria to Teicoplanin. Teicoplanin is a glycopeptide antibiotic effective against a variety of gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Enterococcus spp. These discs are essential for clinical microbiology laboratories conducting antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) to guide therapeutic decisions.
Key Features:
- Active Agent:
- Teicoplanin (30 µg): A glycopeptide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of peptidoglycan precursors.
- Standardization:
- Conforms to EUCAST and CLSI guidelines for antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
- Applications:
- Used in Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion tests to determine bacterial susceptibility or resistance to Teicoplanin.
- Packaging and Quality:
- Individually packaged to ensure sterility and stability.
- Manufactured with consistent and precise antibiotic concentration.
Specifications:
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Teicoplanin TEC Antimicrobial Susceptibility Discs |
| Active Ingredient | Teicoplanin, 30 µg |
| Test Method | Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion |
| Guidelines Compliance | EUCAST, CLSI |
| Target Organisms | Gram-positive bacteria, including MRSA and Enterococcus spp. |
| Packaging | Individually sealed discs |
| Use Case | Determination of bacterial susceptibility |
Use Cases:
- Clinical Microbiology:
- Identify antibiotic susceptibility patterns of gram-positive pathogens such as MRSA, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Enterococcus faecium.
- Monitor the emergence of resistance to Teicoplanin in healthcare-associated infections.
- Pharmaceutical Research:
- Evaluate the efficacy of Teicoplanin against clinical isolates in drug development and pharmacological studies.
- Antibiotic Stewardship Programs:
- Support programs aimed at optimizing antibiotic use by accurately detecting resistant bacterial strains.
- Hospital and Diagnostic Laboratories:
- Standardized testing in routine diagnostics to guide appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Testing Protocol (Kirby-Bauer Disc Diffusion Method):
- Preparation:
- Use Mueller-Hinton agar as the standard medium for testing.
- Inoculate the agar plate with a standardized bacterial suspension (0.5 McFarland standard).
- Application:
- Place the Teicoplanin 30 µg disc on the inoculated agar surface using sterile forceps.
- Incubation:
- Incubate the plate at 35°C ± 2°C for 16-18 hours under aerobic conditions.
- Measurement:
- Measure the diameter of the zone of inhibition and interpret results according to EUCAST or CLSI guidelines.
Advantages:
- Accuracy: Provides precise and reproducible results for antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
- Guidelines Compliance: Adheres to globally recognized standards for AST.
- Versatility: Effective for a wide range of gram-positive bacterial isolates.
- Convenience: Ready-to-use format simplifies laboratory workflows.
References:
- EUCAST Guidelines: European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing.
https://www.eucast.org - CLSI Guidelines: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
https://clsi.org - O’Driscoll, T., et al. "Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): epidemiology, clinical management, and evolution." Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2010.
- Hiramatsu, K., et al. "The emergence and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus." Trends in Microbiology, 2001.
The Liofilchem® Teicoplanin TEC Antimicrobial Susceptibility Discs (30 µg) are indispensable tools for assessing the efficacy of Teicoplanin against gram-positive bacterial pathogens. By enabling standardized and reliable susceptibility testing, these discs support clinical decision-making, research efforts, and antibiotic stewardship initiatives in combating resistant bacterial infections.
Product Specification not found.
Resources file not found.
Add a Review
Customer Review
Tai Tanung - bought Liofilchem® Teicoplanin TEC Antimicrobial Susceptibility Discs, 30 µg
Price??




 0
0