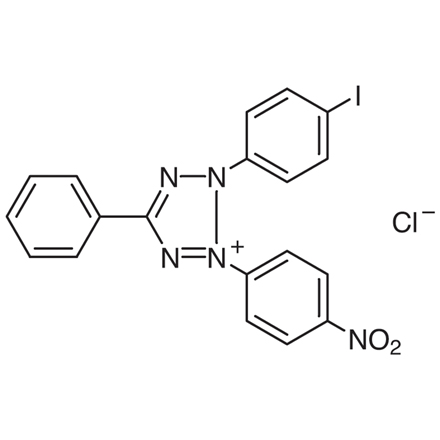
Thermo Scientific™ 2-(4-Iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyltetrazolium chloride 98%
Catalog No :
CAS Number :
Brand :
In Stock
Specifications:
| Application | Colorimetric Assay | ||
| Storage Temperature | 2-8°C | ||
| Product Type | Laboratory Chemical | Forms | Powder |
| Product Brand | Thermo Fisher Scientific™ | ||
| Product Grade | Analytical grade | ||
Thermo Scientific™ 2-(4-Iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyltetrazolium chloride, commonly referred to as INT chloride (≥98% purity), is a highly sensitive, premium-grade biochemical reagent extensively used in metabolic activity and viability assessments across microbiology, cell biology, environmental studies, and biochemical research. Its exceptional purity (≥98%) ensures maximum reliability, accuracy, and reproducibility in sensitive biological assays.
Chemical Specifications
- Chemical Name: 2-(4-Iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyltetrazolium chloride
- Commonly Known As: INT chloride, Iodonitrotetrazolium chloride
- CAS Number: 146-68-9
- Purity Level: ≥98% (highly purified grade)
- Molecular Formula: C19H13ClIN5O2
- Molecular Weight: 505.70 g/mol
- Appearance: Yellow to orange crystalline powder
- Solubility: Soluble in water, aqueous buffer solutions, ethanol, methanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Principle and Mechanism of Action
INT chloride is a tetrazolium salt functioning as a highly sensitive electron acceptor in biological oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. Metabolically active organisms or cells possessing active respiratory enzymes, especially dehydrogenases, enzymatically reduce INT chloride, generating a distinctive purple-red, water-insoluble formazan precipitate.
The formation of formazan directly correlates with the metabolic activity and viability of cells, microorganisms, or enzyme preparations, enabling precise qualitative or quantitative assessments using visual inspection or spectrophotometry.
Applications and Detailed Use Cases
1. Microbial Metabolic Activity and Viability Testing
Primary Use:
- Rapid evaluation of microbial respiration and viability in bacterial, yeast, and fungal cultures.
Practical Example:
- Microbiology laboratories utilize INT chloride to confirm bacterial viability post-antibiotic exposure. Live microorganisms actively reduce INT chloride, producing visible formazan deposits. Reduced formazan formation after antibiotic treatment clearly indicates microbial inhibition or death.
2. Mammalian Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assays
Primary Use:
- Measurement of mammalian cell metabolic activity and viability, particularly in cytotoxicity tests, drug screening, and cell proliferation assays.
Practical Example:
- Cancer researchers incubate human cancer cell lines (e.g., HeLa, MCF-7, or Jurkat) with INT chloride after drug treatment. Cells with intact metabolic function convert INT chloride to formazan, facilitating precise quantification of cell survival and cytotoxic drug efficacy.
3. Enzyme Activity and Metabolic Pathway Research
Primary Use:
- Sensitive detection and quantification of oxidoreductase enzyme activity, particularly NADH-dependent dehydrogenases and mitochondrial enzymes.
Practical Example:
- Researchers studying mitochondrial dysfunction or enzymatic metabolism add INT chloride to isolated mitochondria or cytoplasmic enzyme extracts. The resulting formazan production provides accurate and rapid spectrophotometric measurements of enzyme kinetics and metabolic rates.
4. Environmental Microbiology and Soil Health Assessments
Primary Use:
- Assessing microbial activity and soil biological health through measurement of respiration and metabolic potential in environmental samples.
Practical Example:
- Ecologists employ INT chloride in soil respiration assays to monitor microbial responses to contaminants, bioremediation, or agricultural practices. Enhanced or reduced INT reduction provides a clear indication of microbial ecosystem health and metabolic activity levels.
5. Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Efficacy Studies
Primary Use:
- Detection, quantification, and evaluation of microbial biofilm formation, growth, and antimicrobial susceptibility.
Practical Example:
- Biomedical researchers assessing medical-device-associated biofilms incubate pathogens (e.g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus) with INT chloride on various surfaces. Active biofilms produce visible formazan precipitates, enabling quantification of biofilm density, antimicrobial efficacy, and resistance patterns.
Advantages and Key Benefits
- Ultra-High Purity (≥98%): Delivers enhanced accuracy, sensitivity, and reproducibility across experiments.
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: Enables clear differentiation between viable, metabolically active, and non-active cells.
- Rapid Visual Results: Provides quick visual or spectrophotometric confirmation, ideal for high-throughput applications.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for a wide variety of microbiological, cellular, biochemical, environmental, and biomedical research protocols.
Handling, Storage, and Stability
- Recommended storage: Refrigerated conditions (2–8°C).
- Protect from exposure to direct light, moisture, and contaminants to maintain optimal product integrity.
- Observe laboratory standard safety guidelines for chemical handling.
Intended Users
- Clinical and research microbiology laboratories
- Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies conducting drug discovery and cytotoxicity assays
- Environmental testing and monitoring laboratories
- Academic and industrial biochemical research laboratories
- Researchers in biomedical device development and biofilm management
Thermo Scientific™ 2-(4-Iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyltetrazolium chloride (≥98% purity) is an indispensable reagent designed to provide reliable, precise, and reproducible results, greatly enhancing the quality and accuracy of metabolic, enzymatic, microbiological, and cellular research activities.
- Pack Size: 1g 5g 25g




 0
0